Simulation and Uncertainty Analysis of Nuclide Transport Breakthrough in DFN
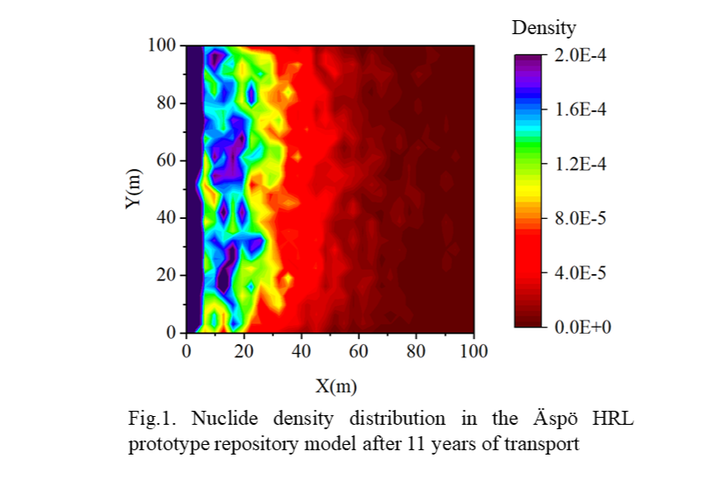
Abstract Understanding the transport of nuclides in fractured rocks is crucial for ensuring biosphere safety, as geological barriers serve as the final line of defense against nuclide transport. A discrete fracture network (DFN) model was constructed based on authentic data from the prototype repository at the Äspö Hard Rock Laboratory (HRL) in Sweden. The model was used to simulate nuclide transport using particle tracking methods and to investigate the spatio-temporal evolution following nuclide leakage. The DFN model has the advantage of providing detailed characterization of fractures, but it also imposes additional uncertainty. The Sobol variance-decomposition method is used to quantify the contribution of the fracture parameters to the uncertainty in the results of flow and transport distance. The results of this research can provide a scientific basis and technical support for the accurate modeling and prediction of the nuclides in geological barriers.
- More Information - PDF.